Overview
Flexography (often abbreviated to flexo) is a form of relief printing and is the method of printing most commonly used for packaging materials (labels, tape, bags, boxes, banners, etc.).
A flexographic print is made by creating a positive mirrored master of the required image as a 3D relief in a rubber or polymer material. A measured amount of ink is deposited upon the surface of the printing plate (or printing cylinder) using an engraved anilox roll whose texture holds a specific amount of ink. The print surface then rotates, contacting the print material which transfers the ink.
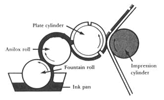
In the typical flexo printing sequence, the substrate is fed into the press from a roll. The image is printed as substrate is pulled through a series of stations, or print units. Each print unit is printing a single color. As with Gravure and Lithographic printing, the various tones and shading are achieved by overlaying the 4 basic shades of ink. These are magenta, cyan, yellow and black. Magenta being the red tones and cyan being the blue.
Flexographic inks are very similar to packaging gravure printing inks in that they are fast drying and have a low viscosity. The inks are formulated to lie on the surface of nonabsorbent substrates and solidify when solvents are removed. Solvents are removed with heat, unless U.V. curable inks are used.
Flexographic printing inks
The nature and demands of the printing process and the application of the printed product determine the fundamental properties required of flexographic inks. Measuring the physical properties of inks and understanding how these are affected by the choice of ingredients is a large part of ink technology. Formulation of inks requires a detailed knowledge of the physical and chemical properties of the raw materials composing the inks, and how these ingredients affect or react with each other as well as with the environment. Flexographic printing inks are primarily formulated to remain compatible with the wide variety of substrates used in the process. Each formulation component individually fulfils a special function and the proportion and composition will vary according to the substrate.